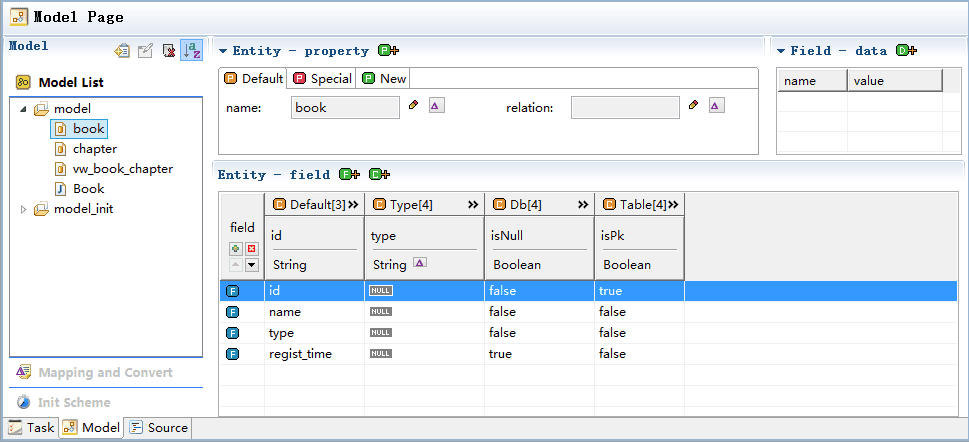
The entity model consists of 2 types of databases and the Java class.
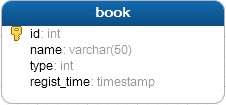
The database has a table book, id is the primary key, including name, type, regist_time fields.

The structure transformed the model is as follows(How to transform the model please read: Model Transform)

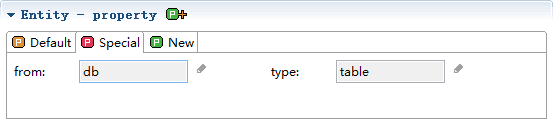
New is the place where the user defines the property itself, where additional properties can be defined.
We can modify the property here, more detailed reading: Property。
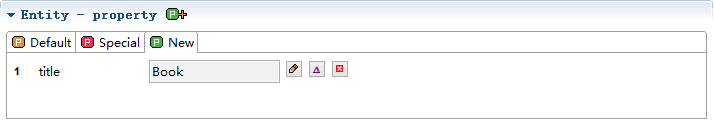
Default
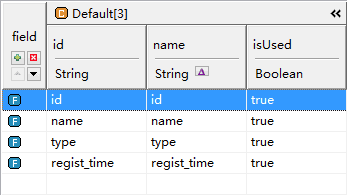
We can modify the value, more detailed reading: Field。
Type: type and fullType are used as the language type and the full type, jdbcType and dbType for the mapping of database types.
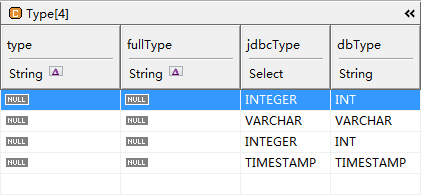
We can modify the value, more detailed reading: Field。
About jdbcType:
There is a big difference between the types of SQL supported by different databases, such as DECIMAL in Oracle, Mysql is not, Mysql varchar type corresponds to Oracle is varchar2. Most databases have their own type rules. Fortunately, the major database vendors are providing their own database jdbc driver, it will follow the jdbc standard, Convert your SQL type to the corresponding jdbc type, which is derived from java.sql.Types. The following are all types: ARRAY, BIGINT, BINARY, BIT, BLOB, BOOLEAN, CHAR, CLOB, DATALINK, DATE, DECIMAL, DISTINCT, DOUBLE, FLOAT, INTEGER, JAVA_OBJECT, LONGNVARCHAR, LONGVARBINARY, LONGVARCHAR, NCHAR, NCLOB, NULL, NUMERIC, NVARCHAR, OTHER, REAL, REF, ROWID, SMALLINT, SQLXML, STRUCT, TIME, TIMESTAMP, TINYINT, VARBINARY, VARCHAR
Db: Some of the properties inherent in the database table and view.

book table has a foreign table chapter, its book_id is a foreign key, associated book table id.
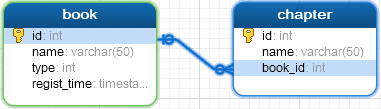
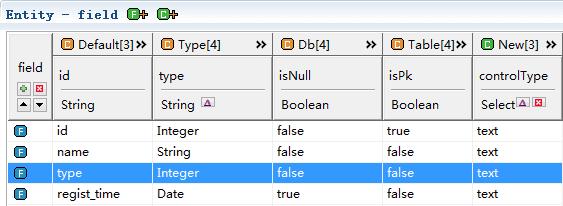
Book table fields id, name, type, regist_time, id is the primary key, so isPk is true.

Chapter table fields id, name, book_id, the primary key is id, so isPk is true, book_id is a foreign key, so isFk is true, the foreign key corresponding to the main table fkEntityName is book, the corresponding field fkFieldName is id.

We can also add new column. The new column is equivalent to adding a new property to each field, in the specific business needs, we also need to add some columns to extend our model.
For example, we need three new columns of fieldName, controlType, isQuery.
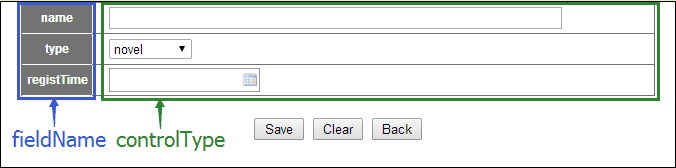
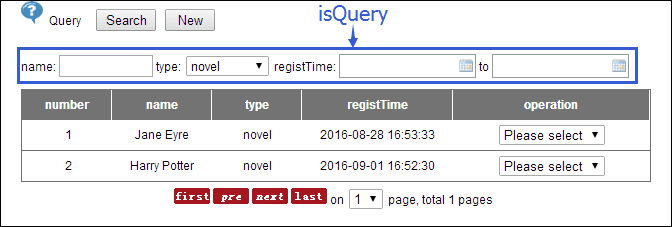
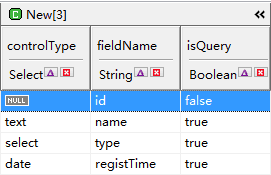
About Column, more detailed reading: column。
Private property for each field, it is data. we can set multiple key values.
When you select any field, you can set its data.
After the selection, you can set the private data of the field.
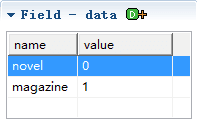
The type field is a drop-down box, select option has 2 items, novel and magazine, value is 0 and 1.
About data, more detailed reading: data。
The database has a view of vw_book_chapter, which is the book table and the chapter join query, the query results are 2 fields name and chapter_name.
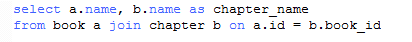
The structure transformed the model is as follows(How to transform the model please read: Model Transform)
We can see that the difference between the view model and the database model is that there is no table part column.
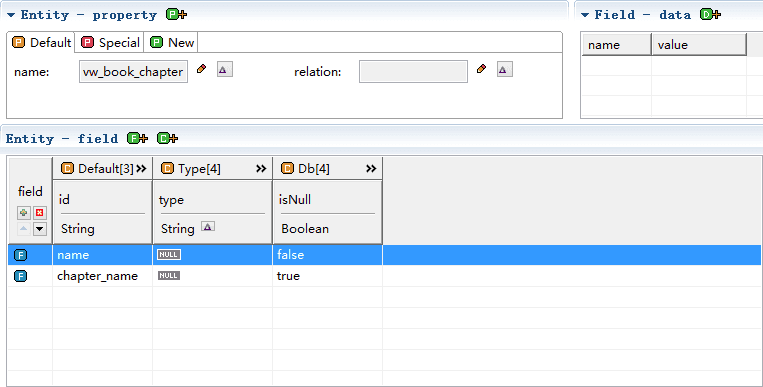
Why not this table part, is well understood, because of view not isPk (key), isFk (foreign) and so on.

The other parts of the view model are the same as the table model.
This class has 4 properties: id, name, type, registTime.
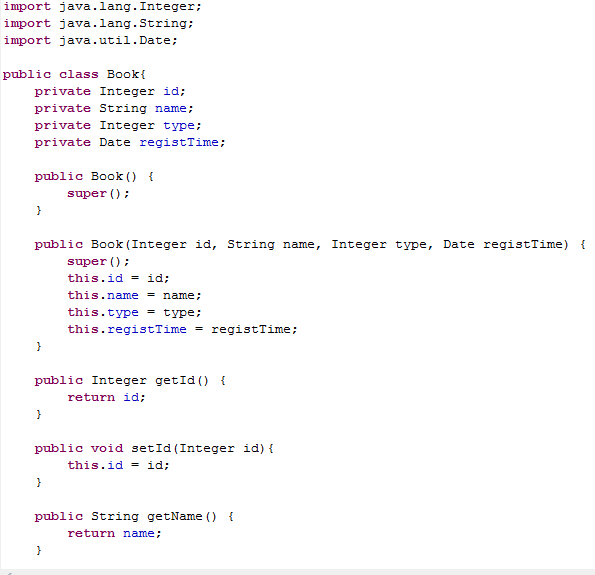
The structure transformed the model is as follows(How to transform the model please read: Model Transform)
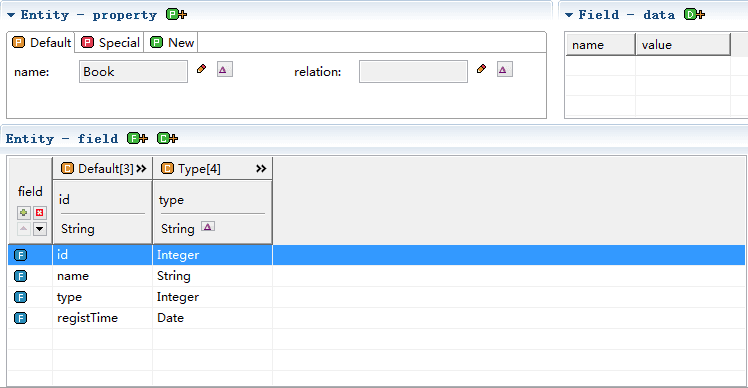
New is the place where the user defines the property itself, where additional properties can be defined.

We can add the property here, more detailed reading: Property。

Default
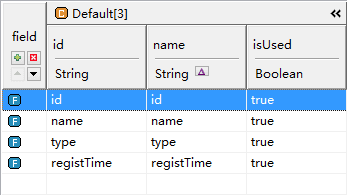
Type: type and fullType are used as the language type and the full type, jdbcType and dbType for the mapping of database types.

Different from the database model, the Java model has only 2 column parts of default and type.
Select the model group in the task, and the relation attribute of the entity tag specifies the model.
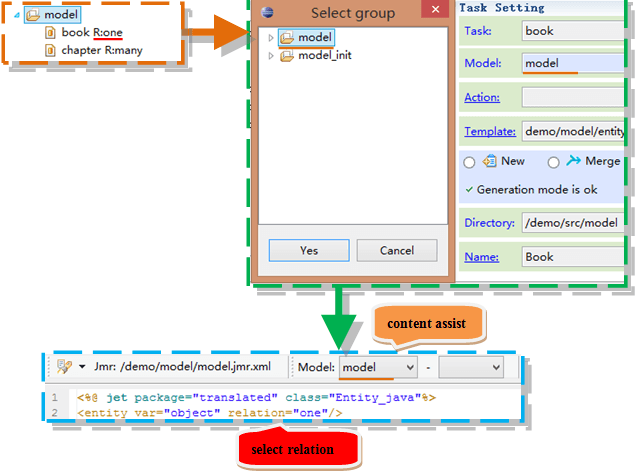
Select the model in the task, entity tag do not specify relation.
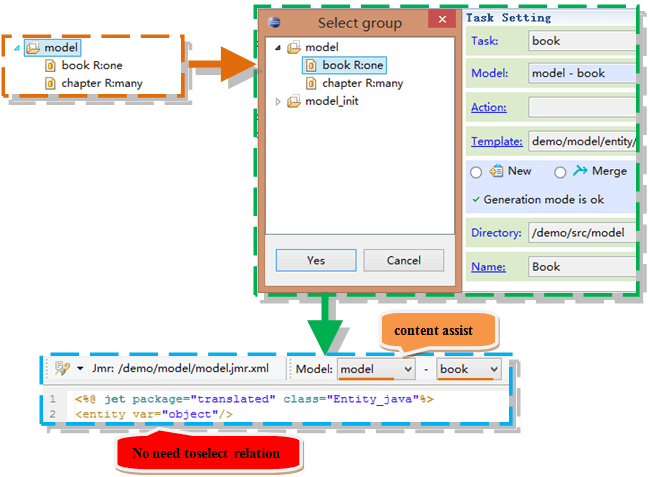
<entity> has 2 attributes
The new variable named object, this object will point to the entity model.
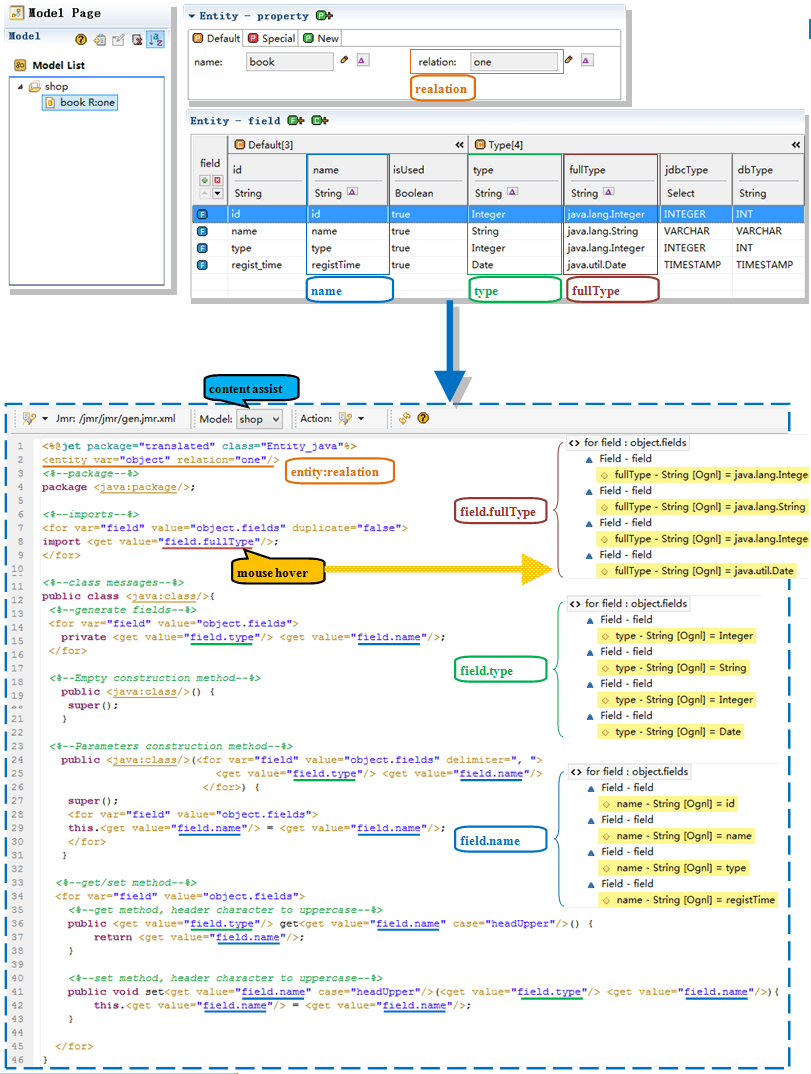
Result

Other tag to be used:
For more use, please read the following: